| Chemistry 211-Exam 3 | Name: | |
| April 23, 1997 | please print |
Answers:
| 1. d | 6. c | 11. b | 16. c |
| 2. a | 7. c | 12. a | 17. a |
| 3. a | 8. a | 13. b | |
| 4. b | 9. d | 14. d | |
| 5. d | 10. d | 15. c |
Solutions:
Instructions: Read the whole examination before starting to work on individual problems. Some problems are easier than others; work those first. Budget your time to insure that you finish the exam ination
1. The partial pressures of CH4, N2, and O2 in a sample were found to be 155, 435, and 122 mmHg respectively. Calculate the mole fraction of methane, CH4.
a. 0.171 |
c. 0.204 |
b. 0.198 |
d. 0.218 |
Solution: Dalton’s law. ![]()
2. According to the kinetic theory of gases, the average speed of molecules is proportional to the
| a. inverse of the square root of molecular mass. | c. square root of the molecular mass. |
| b. inverse of the square root of temperature. | d. temperature |
Solution:
RMS velocity related to temperature by: ![]() .
.
Velocity proportional to inverse of square root of molecular mass.
3. Which atom would be expected to have the lowest ionization energy?
| a. Rb | c. F |
| b. Se | d. Sn |
Solution: Atom with lowest ionization energy should be to the far left; Rb.
4. Which of the following quantum numbers is not permissible?
| a. n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms= +1/2 | c. n = 5, l = 4, ml = - 4, ms= +1/2 |
b. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 2, ms= - 1/2 |
d. n = 2, l = 0, ml = 0, ms= +1/2 |
Solution: b is not permissible since it has an ml > l.
5. Which one of the orbital occupancy designations does not make sense?
a. 2p3 |
c. 1s1 |
b. 3s2 |
d. 2d8 |
Solution: d not possible since cannot have 2d electrons; d electrons only possible when principle quantum number is greater than two.
6. When 907 kg of NH3 is produced, 2.45x106 kJ of heat evolves; determine
D H for the reaction below:N2(g) + 3H2(g)
® 2NH3(g); D H = ?a. - 1.22x106 kJ |
c. - 91.8 kJ |
b. - 45.8 kJ |
d. - 2.45x106 kJ |
Solution:
DH is heat evolved for 2 mol of NH3; heat is proportional to amount of ammonia produced.![]()
7. de Broglie stated that
| a. electrons in an atom have only certain energies. | c. matter has wavelike character. |
| b. no two electrons have same four quantum numbers. | d. elements show periodic trends. |
Solution:de Broglie pointed out the dual nature of matter as having both matter and wavelike characteristics.
8. Atomic titanium should have __ unpaired electrons.
| a. 2 | c. 4 |
| b. 1 | d. 0 |
Solution Ti has d2 electron configuration; Hunds rule indicates they should be in different orbitals.
9. Which atom below would be expected to have the largest radius?
| a. Br | c. F |
| b. Cu | d. Sc |
Solution: Element to the lower left portion of the periodic table; Sc.
10. A 200 g block of iron was heated to 100°C and 200 g of an unknown metal was touched to the block so that heat could flow from the hot one without loss to anything other than the unknown metal. After equilibrium had been obtained, th e temperature of the unknown metal had risen from 25°C to 83°C The unknown metal was
| Cu | 0.385 Jg- 1 °C- 1 | Al | 0.900 Jg- 1 °C- 1 |
Fe |
0.444 Jg - 1 °C- 1 |
Au |
0.129 Jg - 1 °C- 1 |
| a. Cu | c. Al |
| b. Fe | d. Au |
Solution: Heat absorbed by metal is equal to the heat donated by Fe; each heat is given by relationship between its specific heat capacity and its temperature change; find heat capacity of unknown metal and use t hat to determine the identity of the unknown metal. Note that the mass of each metal will cancel since they are the same.
![]()
11. The bonding in water is best characterized as
| a. pure covalent | c. ionic |
| b. polar covalent | d. coordinate covalent |
Solution: Electronegativities of O and H make the bond polar colvalent.
12. In the Lewis structure of ClF3, the number of lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is
| a. 2 | c. 0 |
| b. 3 | d. 1 |
Solution: # val e
- = 4*7 = 28. Lewis dot structure:
13. The geometric arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom
of the ion ![]()
a. tetrahedral |
c. trigonal |
| b. octahedral | d. trigonal bipyramidal |
Solution: 36 val e
- ;octaheral arrangement of e-;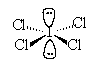
14. The molecular shape of PCl3 is
| a. square pyramidal | c. tetrahedral |
| b. trigonal | d. trigonal pyramidal |
Solution: 26 val e
-; tetrahedral arrangement of electrons but trigonal pyramidal molecular shape.
15. Calculate the wavelength of the first line in the Balmer series (recall that n = 2 for the lower energy state of this series) for hydrogen.
| a. 4.86x10- 7 m | c. 6.56x10- 7 m |
| b. - 4.86x10- 7 m | d. 589 nm |
Solution: ![]()
16. The heat of combustion of toluene, C7H8(l) is
- 3910 kJ. Determine its heat of formation if the heats of formation of CO2(g), and H2O(l) are - 393.51, - 285.83. kJ/mol respectively.| a. - 12.11 kJ/mol | c. 12.11 kJ/mol |
| b. - 2588.7 kJ/mol | d. 2588.7 kJ/mol |
Solution: Write the reaction for the heat of combustion and then use Hess’ law to determine the heat of formation of toluene, t.
1. C7H8(g) + 9O2(g)
® 7CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) DHc =-3910 kJ
2.
DHc = -3910 = 4· (-285.83) + 7· (-393.83) - DHf,t3.
DHf,t = 12.11 kJ.17. Ammonia will burn in the presence of a platinum catalyst to produce nitric oxide.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g)
® 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)What is the heat of reaction at constant pressure? Use the following thermochemical equations:
| N2(g) + O2(g) ® 2NO(g); | D H = 180.6 kJ |
| N2(g) + 3H2(g) ® 2NH3(g); | D H = - 91.6 kJ |
| 2H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2H2O(g); | D H = - 483.7kJ |
| a. - 906.7 kJ | c. - 211.5 kJ |
| b. - 998.3 kJ | d. +998.3 kJ |
| 2N2(g) + 2O2(g) ® 4NO(g); | D H = +361.2 kJ | |
| 4NH3(g) ® 2N2(g) + 6H2(g); | D H = +183.2 kJ | |
| 6H2(g) + 3O2(g) ® 6H2O(g); | D H = -483.7kJ | |
| Sum these to get: | 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ® 6H2O(g) + 4NO(g) | D H = -906.7kJ |