|
Chemistry
212 Exam 3-Key |
Name: |
|
|
May 1, 2000 |
|
please print |
Instructions: Read the whole examination before starting to work on individual
problems. Work the easiest problems
first. Budget your time to insure that you
finish the examination. Don’t waste
time on problems that you find hard to finish until you have worked the
others. Remember the use of
programmable calculators is forbidden and would be considered a serious honor
code violation.
Answers:
|
1. a |
7. b |
13. a |
|
2. c |
8. c |
14. d |
|
3. d |
9. a |
15. b |
|
4. b |
10. b |
16. c |
|
5. d |
11. c |
|
|
6. c |
12. b |
|
Solutions:
1. Which reaction below would result in a net
decrease in entropy?
|
a. 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g)
« 2KClO3(s) |
c. AgBr(s) « Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) |
|
b. CaCO3(s) « CaO(s) + CO2(g) |
d. NH4NO3(s)
« N2O(g)
+ 2H2O(g) |
Solution 1: Look for the reaction that has a smaller number of
moles of gases on the product side.
2. What is the standard cell voltage at 25.0°C for
the reverse of the reaction below?
Pb2+(aq) + Cd(s) «
Pb(s) + Cd2+(aq) K =
1.356x109
|
a. +0.270 V |
c. -0.270 V |
|
b. +0.117 V |
d. -0.117 V |
Solution 2:
![]()
The reverse reaction would develop -0.270
V.
3. Which of the answers below is the correct
representation according to the shorthand method of the following galvanic
cell?
2Fe3+(aq)
+ 3Ni(s) « 2Fe(s) + 3Ni2+(aq)
|
a. Fe3+(aq)|
Fe(s) || Ni(s)| Ni2+(aq) |
c. Ni(s)|Ni2+(aq)
|| Fe(s)| Fe3+(aq) |
|
b. Fe3+(aq)|
Ni(s) || Fe(s)| Ni2+(aq) |
d. Ni(s)|
Ni2+(aq) || Fe3+(aq)| Fe(s) |
Solution 3: Nickel metal is first since it is the anode. Iron metal is last since it is the cathode!
4. What is the solubility of silver
sulfide in water, if it dissolves according to the reaction below?
Ag2S(s) «
2Ag+(aq) + S2-(aq) Ksp = 6.31x10-51
|
a. 6.31x10-51 |
c. 9.28x10-18 |
|
b. 1.16x10-17 |
d. 1.28x10-17 |
Solution 4:
![]()
5. Using Boltzmann’s formula,
calculate the entropy of 1.563x1010 molecules of a compound if they
are randomly distributed in one of two ways.
|
a. DS
= 4.16x10-24 J/K |
c. DS = 6.50x10-14
J/K |
|
b. DS
= 9.01x1010 J/K |
d. DS = 1.50x10-13
J/K |
Solution 5: determine the number of moles and then use the
Boltzmann relationship.

![]()
6. What is the free energy change at 25.0°C for the reaction below, if
the standard entropies of reactants and products are So(C(gr)) =
5.74 J/mol×K, So(H2(g)) =
130.68 J/mol×K and So(C6H6(l))
= 173.30 J/mol×K and the heat of formation of C6H6(l)
is 49.00 kJ/mol.
6C(gr) + 3H2(g) «
C6H6(l)
|
a. DGo
= -1.24x102
kJ |
c. DGo =
1.24x102 kJ |
|
b. DGo = -26.448
kJ |
d. DGo = 26.448 kJ |
Solution 6: DG = DH - TDS. You are given DH;
calculate DS from the given entropies of reactants
and products.
DS
= 173.3 - (3×130.68
+ 6×5.74) = -253.3
J/K
DG
= 49.00 - 0.29815×(-253.3)
= 124.4 kJ
7. What is the molar
concentration of ![]() when an excess of
solid mercury (I) chloride is added to 0.186 M NaCl so that some solid
remains? The solubility reaction is: Hg2Cl2(s)
«
when an excess of
solid mercury (I) chloride is added to 0.186 M NaCl so that some solid
remains? The solubility reaction is: Hg2Cl2(s)
« ![]() (aq) + 2Cl-(aq) Ksp = 1.288x10-18
(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) Ksp = 1.288x10-18
|
a. 4.81x10-7 M |
c. 1.79x10-19 M |
|
b. 3.73x10-17 M |
d. 3.53x10-20 M |
Solution:

8. The free energy of formation
for C6H6(g) is 129.72 kJ/mol. What is the equilibrium constant at 25.0°C for its formation?
|
a. 4.60x10-53 |
c. 1.88x10-23 |
|
b. 2.18x10+52 |
d. 5.32x10+22 |
Solution: Remember the relationship between free
energy change and the equilibrium constant.
![]()
9. What is the
cell voltage for the following cell?
Sn2+(aq) + Mg(s) «
Sn(s) + Mg2+(aq) DGo
= -430.3 kJ
|
a. +2.23 V |
c. -2.23 V |
|
b. +0.14 V |
d. -0.14 V |
Solution: 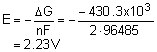
10. What is the standard cell
potential for the following cell? Will
the reaction be spontaneous?
|
Ni(s) + Mg2+(aq) « |
Ni2+(aq) + Mg(s) |
|
|
Ni2+(aq) + 2e- « |
Ni(s) |
Eo = -0.260 V |
|
Mg2+(aq)
+ 2e- « |
Mg(s) |
Eo = -2.370 V |
|
a. +2.110 V, spontaneous |
c. +4.220 V, non-spontaneous |
|
b. -2.110 V, non-spontaneous |
d. -4.220 V, spontaneous |
Solution:
![]() . Negative voltage means
that the reaction is non-spontaneous.
. Negative voltage means
that the reaction is non-spontaneous.
11. What must be the reaction
quotient, Q, if the free energy is -243.56
kJ at 25.0°C?
2C2H2(g) + H2(g)
« C4H6(g) DGo = -216.79
kJ
|
a. 0.26 |
c. 2.03x10-5 |
|
b. 2.82x10-5 |
d. 1.32x10-25 |
Solution:

12. What is the molar
concentration of Al3+(aq) if the cell potential was 0.872 V and the
molar concentration of Cr3+(aq) is 8.18x10-5
M?
Cr3+(aq) + Al(s) «
Cr(s) + Al3+(aq) ![]() V
V
|
a. 2.70x10-2 M |
c. 9.73x10-5 M |
|
b. 2.26x10-2 M |
d. 9.40x10-4 M |
Solution: Use the Nernst equation.
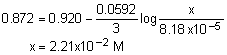
13. Calculate ![]() for C8H10(g)
at 25.0°C from the information below, if
for C8H10(g)
at 25.0°C from the information below, if ![]() (CH4(g)) is -50.79
kJ/mol.
(CH4(g)) is -50.79
kJ/mol.
8CH4(g) «
C8H10(g) + 11H2(g) DGo = 534.56 kJ/mol
|
a. +128.0 kJ |
c. +16.303 kJ |
|
b. -16.030 kJ |
d. -128.0 kJ |
Solution: ![]()
![]()
14. What is the total entropy change at 25.0°C for
the reaction below, if the standard entropies of reactants and products are So(C(gr))
= 5.74 J/mol×K, So(H2(g)) =
130.68 J/mol×K, and So(C10H10(l))
= 368.99 J/mol×K and the heat of formation of C8H10(g)
is 29.80 kJ/mol.
8C(gr) + 5H2(g) «
C8H10(g)
|
a. -330
J/K |
c. +430 J/K |
|
b. +330 J/K |
d. -430 J/K |
Solution: DS = 368.99 J/K - (5×130.68 J/K + 8×5.74 J/K) = -330 J/K.
![]()
15. Which of the combinations
below will not produce any precipitate?
The concentrations shown are after mixing, but before reaction.
|
a. 3.37x10-7 M Pb(NO3)2
+ 1.35x10-4 M Na2CrO4;
Ksp(PbCrO4) = 2.818x10-13 |
|
b. 1.72x10-7 M AgNO3
+ 1.96x10-15 M NaBr; Ksp(AgBr)
= 5.495x10-13 |
|
c. 3.47x10-20 M Bi(NO3)2
+ 6.96x10-14 M Na2S;
Ksp(Bi2S3) = 1.000x10-97 |
|
d. 1.34x10-16 M CuNO3
+ 1.87x10-14 M Na2S;
Ksp(Cu2S) = 1.995x10-47 |
Solution: Determine Qsp
for each. If Qsp < Ksp,
there will be no precipitate. By
inspection one can see that answer b meets this criterion.
16. How many grams of tin metal
will be plated out in an electrolysis system operated at 6.050 A for 251.8
seconds from a solution containing Sn2+(aq)
|
a. 6.651x10-5 g |
c. 0.937 g |
|
b. 0.838 g |
d. 2.561x10-2 g |
Solution: ![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|